testicle torsion test|how to diagnose testicular torsion : distribute Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of . Tudo que você precisa fazer agora é selecionar o arquivo ou aplicativo que deseja enviar. Em seguida, pressione e selecione Long, e escolha Steg na lista de aplicativos de compartilhamento. Depois de selecionar o Steg, basta tocar no botão Encode mostrado na tela do seu telefone. Você receberá uma mensagem de notificação quando a .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 23 de ago. de 2023 · A primeira coisa que você deve fazer é visitar o Site Oficial do PPSSPP em https://www.ppsspp.org. A partir daí, você pode .
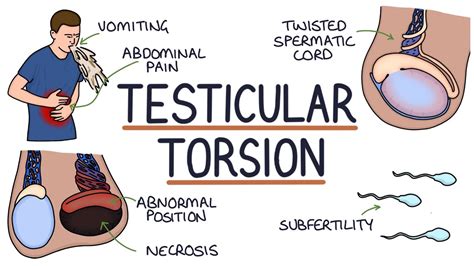
Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of . Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to . Testicular torsion is a true urologic emergency, and early identification is critical to prevent the need for testicular amputation. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to .
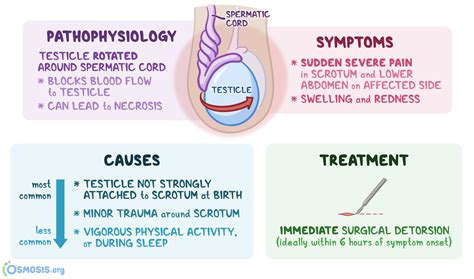
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Testicular torsion is the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. It is a urological emergency requiring urgent surgical intervention . It can either be due to an intravaginal (‘bell-clapper deformity’) or extravaginal cause. Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and.
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. . Tests that can be used to .Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .
testicular torsion signs on examination
Investigations. The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration.. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity. The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes). A history and physical exam consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consult for scrotal exploration. If history and physical exam suggest testicular torsion, immediate surgical consultation and exploration should take precedence over diagnostic tests. Usually affects young males but may affect males of any age.
↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord .Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of
The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion.Testicular torsion has an annual incidence of approximately 1 in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. 1 It is more common in children and adolescents, and delayed repair can result in the loss of .Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.
American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices.Testicular torsion is an emergency: When it happens, . This normally causes the testicle to contract, which probably won't happen if you have a testicular torsion. The doctor also might do tests to see if the spermatic cord is twisted, including: Ultrasound. High-frequency (Doppler) waves are used to make an image of the testicle and check .Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have .
Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . A healthcare professional may also test the patient’s cremasteric reflex, which is highly effective in helping diagnose .1: Epididymis 2: Head of epididymis 3: Lobules of epididymis 4: Body of epididymis 5: Tail of epididymis 6: Duct of epididymis 7: Deferent duct (ductus deferens or vas deferens). Prehn's sign (named after urologist Douglas T. Prehn) [1] is a medical diagnostic indicator that was once believed to help determine whether the presenting testicular pain is caused by acute .
testicular torsion signs and symptoms
The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is twisted. If blood flow is higher than typical, this can help confirm that you have epididymitis.
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion in Pediatric Acute Scrotum: A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test Study. J Urol .
How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age.Testicular torsion in young boys and teen boys occurs when the testicles are not completely attached in the scrotum. This lets the testicles move more freely and twist. . He may also have tests, such as an ultrasound. This is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to see the scrotum and testicles and check blood flow.Testicular torsion can occur at any age but commonly occurs soon after birth or between the ages of 12–18 years with a peak in incidence at age 13–14 years. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and sessions of hemocoagulation) required .Testicular torsion must be considered in any patient who complains of acute scrotal pain and swelling. Torsion of the testis is a surgical emergency because the likelihood of testicular salvage .
To do a testicular self-exam, stand unclothed in front of a mirror. Then: Look for swelling. Hold your penis out of the way and examine the skin of the scrotum. Examine each testicle. Using both hands, place your index and middle fingers under the testicle and your thumbs on top. Gently roll the testicle between your thumbs and fingers.
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle twists around the cord (the structure extending from the groin to the testes that contains the sperm ducts and blood vessels), like an apple twisting on its stem. When the blood vessels are twisted, they can cut off circulation to the testicle and cause permanent damage, including death of the . Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates around the spermatic cord, which provides blood to the scrotum (a bag of skin that contains the testicles). Testicular torsion typically affects adolescents, although it can occur at all ages, including newborns and older adults. . Additional diagnostic methods include urine tests to exclude .Testicular torsion can occur at any age, although it is more common in the first year of life and at puberty (peak age being 12-18 years). Testicular torsion can even occur before birth (during the prenatal period). Left testicle torsion is more common than right testicle torsion. The exact cause of testicular torsion is not known.
Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage the testicle, causing .
testicular torsion prognosis
is testicular torsion obvious
webVenha para o Cassino on-line da LV BET! ♠️ Divirta-se em jogos de cassino e slots com jackpots e aumente seus ganhos nas promoções! Jogue e ganhe na LVBET.com!
testicle torsion test|how to diagnose testicular torsion